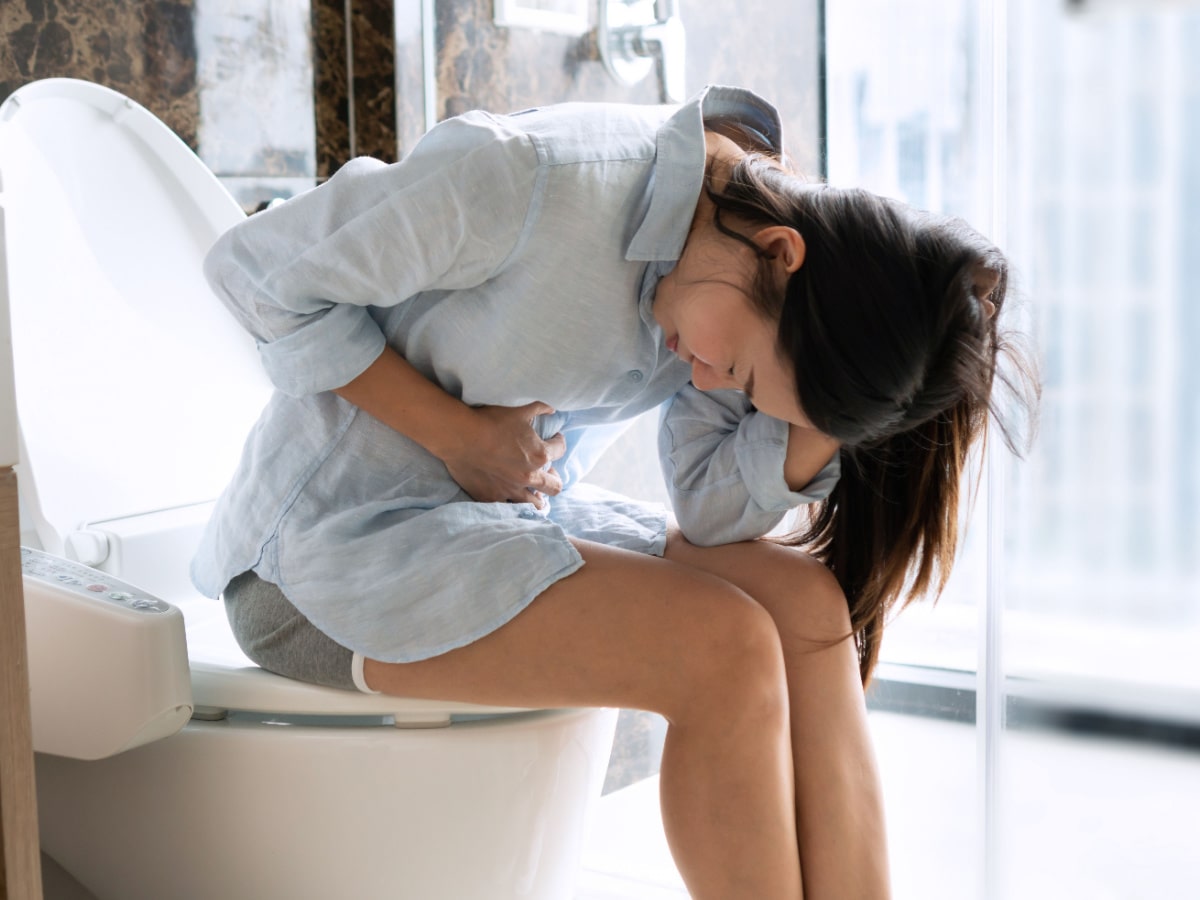
Mucus in your stool can lead to worry about the cause and if you need to see a doctor urgently. By itself, this gut symptom is not a sign of a more serious digestive condition, however, it does indicate a certain degree of irritation in the bowel.
Going to the toilet is something most of us prefer to keep private, but there’s no shame in having an occasional question about bowel movements. The form of the stool (poo) can provide some helpful information about the health of the gut.
This guide will explore the possible causes of mucus in stool, the symptoms that may be present as well as when you may need to speak to a healthcare professional.
Mucus in stool can commonly accompany gut issues such as IBS, SIBO and IBD. The appearance of mucus in stool can also be caused by certain medications or food allergies.
What is Mucus in the Stool?
When you see mucus in the stool it may seem abnormal however, mucus is a normal part of the gut and is constantly produced in small amounts. It was originally understood that that the main role of this mucus was to make it easier for food to travel through the bowel. We now know this mucus is more complex.
When your gut is healthy a very thin layer of mucus coats the gut lining. This layer of mucus is about 0.1mm thick and serves a range of purposes.
These include:
- Forming a protective barrier along the gut lining.
- Mucus contains anti-microbial compounds to keep less beneficial bacteria in lower levels.
- Mucus can be used as an energy source for beneficial gut bacteria.
This level of mucus can increase and become visible in the stool if the bowel becomes irritated. The simplest way to consider this is that if the gut feels irritated or under threat, it produces more mucus to protect itself. [Source: BMJ]
It has also been found that there are more mucus-producing cells in the large intestine. This is likely linked to there being more bacteria in the large intestine.
What does it look like?
Mucus can look gel-like, slimy and in some cases stringy. It may also be similar to the mucus produced in the throat when unwell.
Colour wise, if you have noticed mucus in the stool this can be white, clear or perhaps cloudy. It may also be other colours which may point to other bowel issues. These will be explored later in this article.
Mucus is also commonly seen as covering parts of the stool on the surface but can also be present within the stool.
If your experience high levels of digestive symptoms it’s also possible for mucus to be passed without a stool. Simply said, this is where only mucus is passed when going for a poo.
What Causes Mucus in Stool?

The role of mucus is to protect the bowel wall. Therefore factors that irritate the gut and increase its need for protection can lead to more mucus being produced.
There are several factors that can be responsible for this increased irritation that we’ll explore here.
The most common causes of mucus in stool include:
- Food allergies
- IBS
- Gut Infections
- IBD
Mucus in stool can be a sign of various health conditions. Small amounts are normal, but larger amounts, especially with diarrhea, may indicate infections. If accompanied by blood or abdominal pain, it could signal serious issues like Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, or even colorectal cancer.
Food allergies
Food allergies occur when the immune system reacts to a food. This immune response can trigger inflammation in your digestive tract which results in excess production of mucus from the lining (mucosa).
A study found that 60% of the participants with food-related gut issues experienced mucus as one of their main symptoms.
Alongside the presence of mucus 41% experienced joint swelling and 71% experienced joint pain. This indicates that even though food allergies can lead to gut symptoms, it’s also possible for them to lead to other types of non-digestive symptoms due to gut irritation. [Source: PubMed]
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
IBS is characterized by abdominal pain accompanied by diarrhoea or constipation along with other symptoms such as bloating and abdominal pain. Mucus can be a common symptom of IBS.
This can also be related to food allergies but IBS causes can commonly be related to changes in the gut bacteria (such as SIBO or dysbiosis) or low-grade inflammation following food poisoning or a digestive infection. [Source: PubMed]
Gut Infections
Many types of bacterial infections may cause mucus in stool. Bacterial infections most commonly occur when you have an imbalance between good and bad bacteria in your intestines (dysbiosis).
These types of imbalances make the gut less stable and less resilient to infection.
These infections can include Clostridium difficile colitis, Shigella infection (shigellosis), Salmonella enterocolitis or giardia. [Source: PubMed, PubMed]
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Mucus in the stool can be commonly seen in Inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative colitis.
This can be due to the inflammatory and irritation along the lining of the gut small or large intestine. [Source: PubMed]
Other symptoms of this inflammatory bowel disease include:
- Weight loss
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhoea
- Blood in the stool [Source: PubMed]
If you have seen your doctor about your symptoms, you may already have been tested for inflammatory bowel diseases such as Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative colitis.
Symptoms to look out for
Other symptoms that can be present with mucus can be those typically seen in IBS and SIBO.
These include:
- Bloating and distention
- Abdominal pain
- Flatulence
- Cramping
- Urgency and diarrhoea
- Constipation
- Pain in the lower left of the abdomen
These are in-line with the general symptoms seen along with mucus. There are also additional symptoms that may mean medical assessment is needed. [Source: PubMed]
When to seek medical advice

Seeing mucus in the stool is not something to ignore. However, there are other symptoms that may require a more urgent medical appointment.
These are considered red flag symptoms and can be a sign of a more serious underlying issue.
These symptoms include:
- sudden change in bowel habit
- rectal bleeding or bloody stools
- unintentional weight loss
- iron deficiency anaemia [Source: NICE]
Mucus in Stool Diagnostic Process
When mucus is present, working to assess the underlying issue is a key part of the approach.
So rather than taking medication to suppress or reduce this symptom, understanding what’s irritating the bowel in the first instance.
These tests can be carried out in a nutrition clinic or at home via a home testing kit which is then posted back to the lab for processing.
In cases where red flag symptoms are also present, a colonoscopy may also be arranged which would need to be carried out in a hospital setting.
Gut Tests for Mucus in the Stool
For the most part, this increase in mucus is visible to the eye. Particularly if you are reading this article, it’s likely that you have spotted mucus in your toilet bowel. So while mucus is visible, the underlying irritation or imbalances in the gut, are not likely visible to the eye.
It’s these microscopic changes in the bowel that gut tests will be assessing. For example changes in the balance of the bacteria, overgrowth of bacteria, infections and inflammation can’t be diagnosed solely based on symptoms.
When working to find the cause of the higher levels of mucus appearing in the stool, various tests can be considered.
These include:
- SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth) breath test [Source: PubMed]
- Calprotectin test (to assess for inflammation) [Source: NHS]
- Food intolerance testing [Source: PubMed]
- Nickel Allergy [Source: PubMed]
- Colonoscopy [Source: PubMed]
- CT scan [Source: PubMed]
Treatment Options for Mucus in the Stool
The treatments for mucus in stool should not target the mucus itself, but the underlying cause of the increased mucus production. The exact treatment can depend on the underlying factors and how they need to be approached.
IBS Mucus Treatment
With IBS, approaches such as peppermint oil, probiotics and prebiotics have been well studied and found to improve and wide range of gut health issues.
These supplements include:
- Probiotics [Source: PubMed]
- Prebiotics [Source: PubMed]
- Glutamine [Source: PubMed]
- Peppermint oil [Source: PubMed]
- Antimicrobial herbs [Source: PubMed]
The Low FODMAP diet can also be considered as a form of symptom management, however, this diet will not address the underlying issue in the bowel.
While fibre is the part of plants that our bodies can’t digest, but it’s great for keeping us regular and healthy. However, if the bowel is irritated, this fibre may cause further irritation. This is the reason we use the low FODMAP diet as a short-term symptoms management strategy.
Read more about the Low FODMAP Diet
IBD Mucus Treatment
In those with inflammatory bowel disease many natural approaches are available. These include high-strength probiotics as well as anti-inflammatory supplements such as omega-3 fish oils and curcumin. [Source: PubMed]
Additionally, due to the inflammation and immune situation in those with inflammatory bowel conditions, diet can form a more central part of a treatment. This can be with diets such as:
Infection Mucus Treatment
If the mucus is present due to an underlying infection in the bowel then antibiotics may need to be used for treatment. For many, this can reinforce the need for a clear diagnosis before treatment.
These infections include:
Some gut infections such as food poisoning can be self-limiting, which means they can resolve by themselves without medical intervention. However, others may require antibiotic treatment, especially if symptoms persist. After treatment, retesting is usually considered to confirm that the medications have been successful [Source: PubMed]
Preventative Measures and Tips
Different approaches to gut health can be needed depending on the symptoms and the balance of the gut. This is perhaps why the internet can be a very confusing place to learn about gut health.
If you are not currently experiencing symptoms and want to keep your gut as healthy as possible a high fibre, high FODMAP diet that is low in processed and refined foods is considered the best approach.
This type of diet will contain a wide range of gut-friendly fibres and diverse polyphenols to keep the gut nourished and resilient. For long-term gut health maintenance, this is the type of diet that is suggested to patients.
(However, if symptoms are present and the gut is sensitive, fibre may need to be reduced with a Low FODMAP diet to attempt to reduce symptoms!)
It’s also known that so many factors that are great for all areas of human health are also extremely important of gut health.
These include ways to focus indirectly on the gut to improve microbial diversity. This is a key way to assess the health and the resilience of the gut microbiome and a key way to reduce the risk of symptoms developing.
Perhaps less well-known strategies to improve microbial diversity and gut health include:
- Adequate sleep [Source: PLOS]
- Stress management and relaxation [Source: Springer]
- Time in nature [Source: PubMed]
- Sunlight exposure [Source: Tandfonline]
- Limiting exposure to chronic noise [Source: PubMed]
Next Steps
Mucus in stool is a common symptom that indicates an irritation in the bowel.
If you are experiencing this symptom or any of the other digestive symptoms mentioned in this article, book a free assessment with our gut health specialists.
FAQs
Can stress cause mucus in the stool?
A range of factors can lead to changes in bowel function, with stress being a key factor.
Stress can impact gut health in a number of ways. These include increasing inflammation as well as impacting the integrity of the gut lining. [Source: PubMed, PubMed]These factors may then lead to a degree of irritation that can contribute to increased production of mucus in the stool.
Why does mucus come out when I fart?
A mucus is a protective barrier that helps to protect your body from bacteria and viruses However, if the gut lining is irritated, more mucus may be produced. This can build-up within the digestive tract.
For many, this mucus may be produced towards the end of the bowel or accumulate there. Therefore, it can be present when gas is passed. [Source: PubMed]
If you’re experiencing mucus in stool, it could be due to an underlying condition such as ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease (both of which cause inflammation in the digestive tract). If this happens regularly or if there are other symptoms associated with these conditions.
Why do I have jelly-like mucus when I wipe my bum?
You may have noticed mucus in your stool, which can be a sign of inflammation. This can be caused by a number of conditions including irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and bacterial infections.
In the case of IBS, there is no structural damage to the intestines but they become irritated due to increased secretions from the intestinal tract. The excess production of mucus can often be present alongside symptoms such as diarrhoea or constipation. [Source: PubMed]
What Colour is IBS mucus?
The mucus in the stool is usually white or yellow, and it can be smelly. It may be thick, sticky and stringy. Mucus in your stool is a common symptom of an intestinal infection, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and food poisoning.
If there is blood present in the bowel, this can also influence the colour of the mucus in the stool. This can lead the mucus to range from light pink to a darker shade of pink or red. [Source: PubMed]
What does mucus in stool indicate?
Mucus in the stool can be a sign of irritation or inflammation. It can be caused by bacterial, viral or parasitic infections; food allergies; inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and even irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). [Source: PubMed]
Mucus is produced by the body’s mucosal linings. This includes the mouth, nose, throat and gastrointestinal tract. The role of this mucus is both a form of protection as a physical barrier but it also contains compounds that can kill or neutralise invading pathogens. [Source: PubMed ]